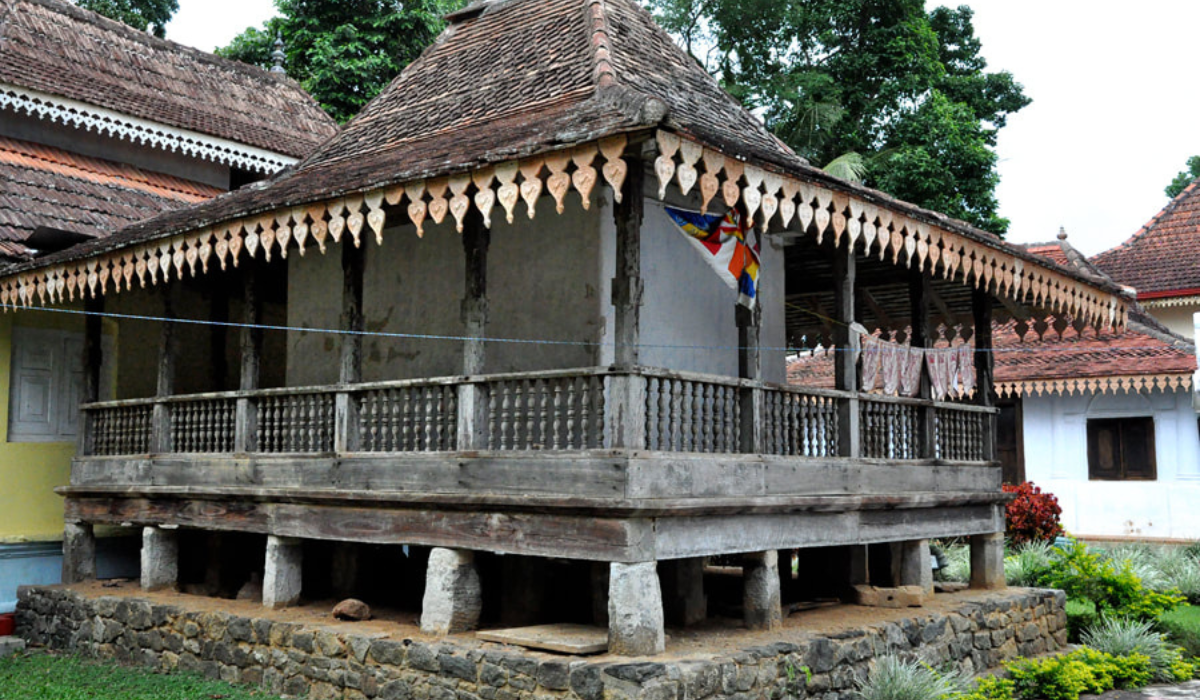
Anuradhapura is home to numerous architectural marvels that reflect the grandeur of its past. The city boasts some of the most impressive stupas, monasteries, and palaces in Sri Lanka, which attract tourists and pilgrims from around the world.
Introduction
Table of Contents
Sri Lanka, a land steeped in history and culture, boasts numerous ancient cities that bear testament to its rich heritage. Among these, the Kingdom of Anuradhapura stands out as a significant historical city and a center of Buddhism. This article delves into the history of the Kingdom of Anuradhapura, its cultural significance, traditional practices, and other captivating aspects that make it an attractive tourist destination.
Historical Overview of the Kingdom of Anuradhapura
The Founding of Anuradhapura
The Kingdom of Anuradhapura was founded in the 4th century BCE by King Pandukabhaya, who established it as the first capital of ancient Sri Lanka. This marked the beginning of one of the longest and most influential periods in Sri Lankan history, lasting over 1,300 years until the 10th century CE. The city was named after a minister called Anuradha and became the political and religious center of the island.
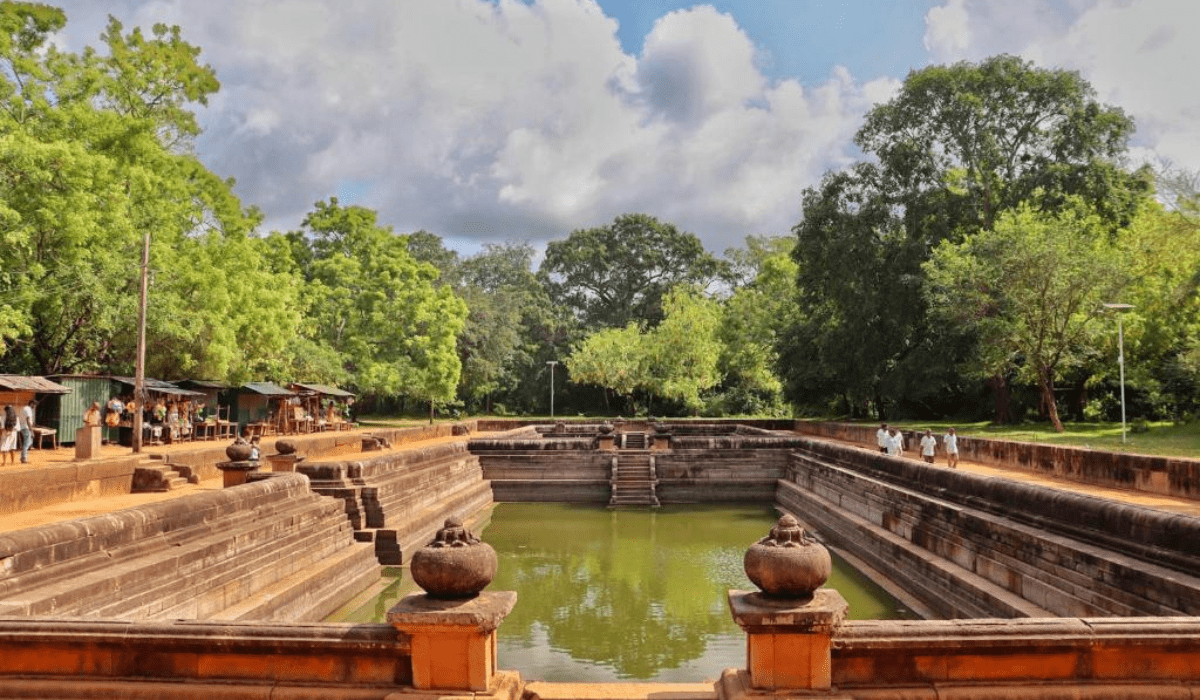

The Development of the Kingdom
Under the rule of successive kings, Anuradhapura flourished as a major center of politics, culture, and religion. The city was meticulously planned with a complex irrigation system, which included the construction of large reservoirs and canals to support agriculture. This sophisticated infrastructure not only ensured the prosperity of the kingdom but also showcased the advanced engineering skills of ancient Sri Lankans.
Prominent Kings and Their Contributions
King Devanampiya Tissa (247-207 BCE):
One of the most significant rulers of Anuradhapura, King Devanampiya Tissa, is credited with introducing Buddhism to Sri Lanka. His reign saw the arrival of Mahinda Thera, the son of Emperor Ashoka of India, who played a pivotal role in spreading Buddhism on the island.
King Dutugemunu (161-137 BCE):
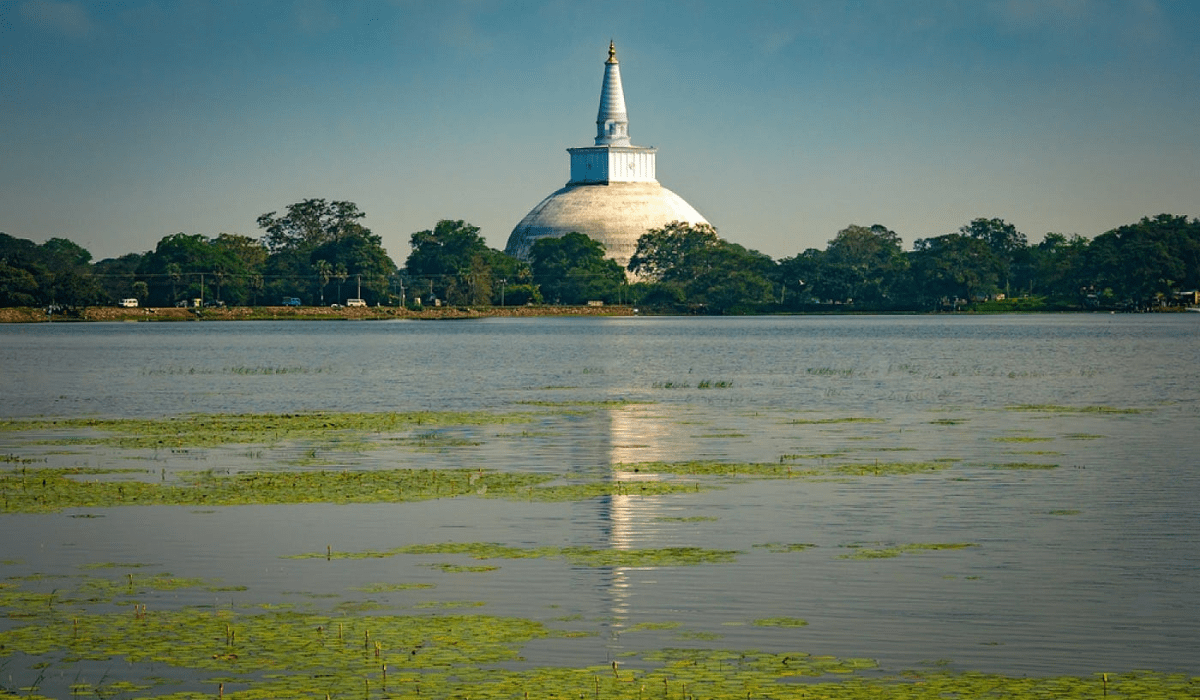
Known for his military prowess and dedication to Buddhism, King Dutugemunu unified the country by defeating the South Indian invader King Elara. He is celebrated for constructing the Ruwanwelisaya, one of the largest stupas in Sri Lanka, which remains a major pilgrimage site.
King Mahasena (274-301 CE):
Renowned for his contributions to irrigation, King Mahasena built several large reservoirs, including the Minneriya Tank, which is still in use today. He also constructed the Jetavanaramaya stupa, which was once the tallest stupa in the world.

The Decline of Anuradhapura
The Kingdom of Anuradhapura began to decline in the 10th century due to repeated invasions by South Indian dynasties such as the Cholas. The continuous threat from invaders eventually led to the abandonment of Anuradhapura as the capital. The capital was moved to Polonnaruwa in the late 10th century, marking the end of Anuradhapura’s prominence as the political center of Sri Lanka.
Cultural Significance of Anuradhapura
Architectural Marvels
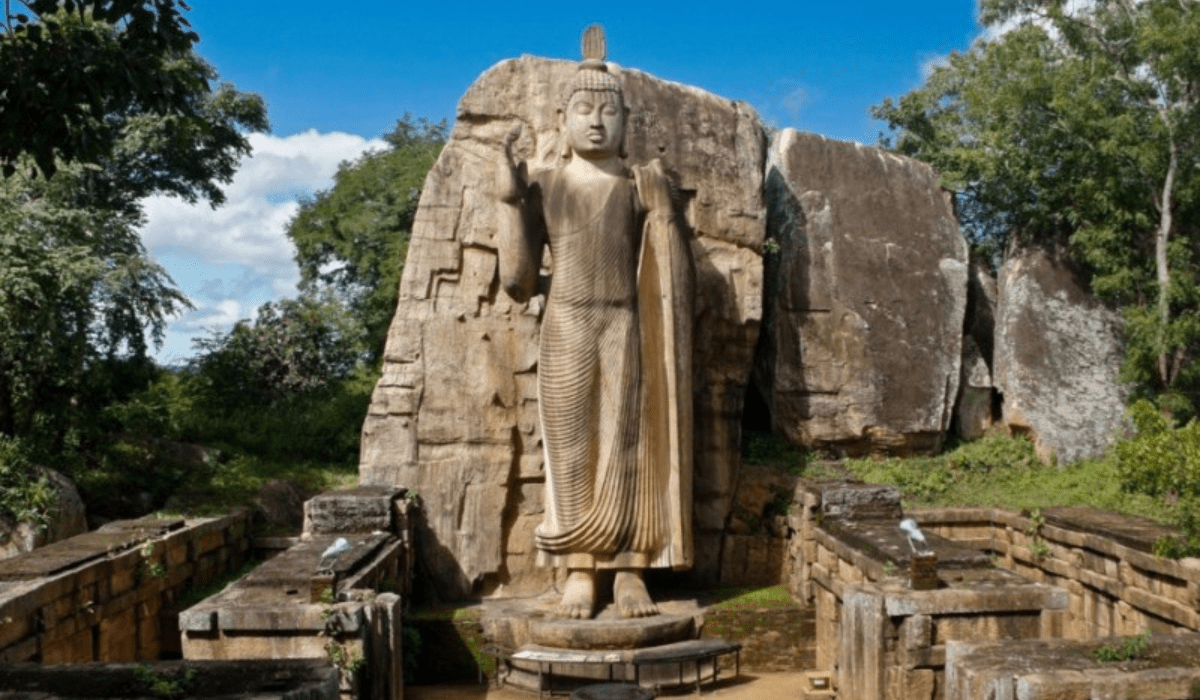
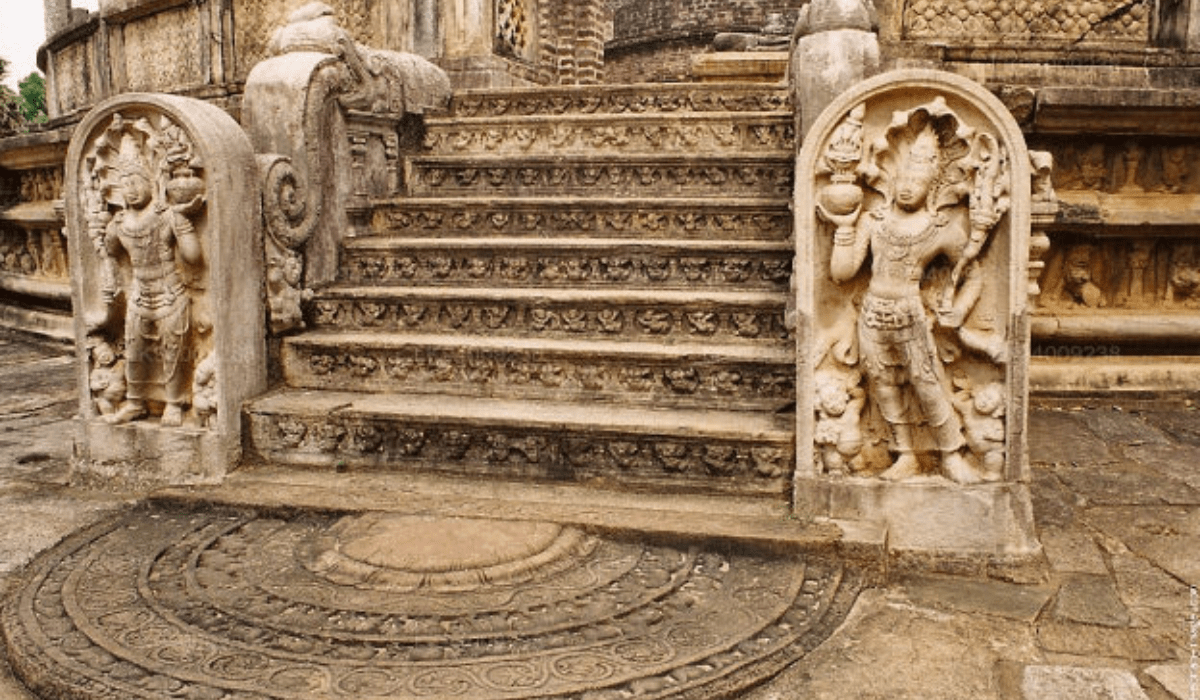
Anuradhapura is home to numerous architectural marvels that reflect the grandeur of its past. The city boasts some of the most impressive stupas, monasteries, and palaces in Sri Lanka, which attract tourists and pilgrims from around the world.
- Ruwanwelisaya: Built by King Dutugemunu, this stupa is one of the most sacred Buddhist sites in Sri Lanka. It is renowned for its massive size and architectural beauty, symbolizing the zenith of stupa construction in ancient Sri Lanka.
- Jetavanaramaya: Constructed by King Mahasena, this stupa was once the tallest brick structure in the world. It stands as a testament to the engineering and architectural prowess of ancient Sri Lankans.
- Thuparamaya: Believed to be the first stupa built in Sri Lanka following the introduction of Buddhism, Thuparamaya enshrines the collarbone relic of the Buddha and is an important pilgrimage site.
Religious and Cultural Hub
Anuradhapura was not only a political center but also a major religious and cultural hub. The city played a crucial role in the spread and development of Theravada Buddhism in Sri Lanka. Monasteries, such as the Mahavihara, Abhayagiri, and Jetavana, served as centers of Buddhist learning and practice, attracting monks and scholars from across the Buddhist world.
Traditional Practices and Activities
Buddhist Pilgrimage
Anuradhapura remains a significant pilgrimage site for Buddhists. Pilgrims visit the city to pay homage to its numerous sacred sites, including the ancient Bodhi Tree, which is said to be a sapling of the original Bodhi Tree under which the Buddha attained enlightenment.
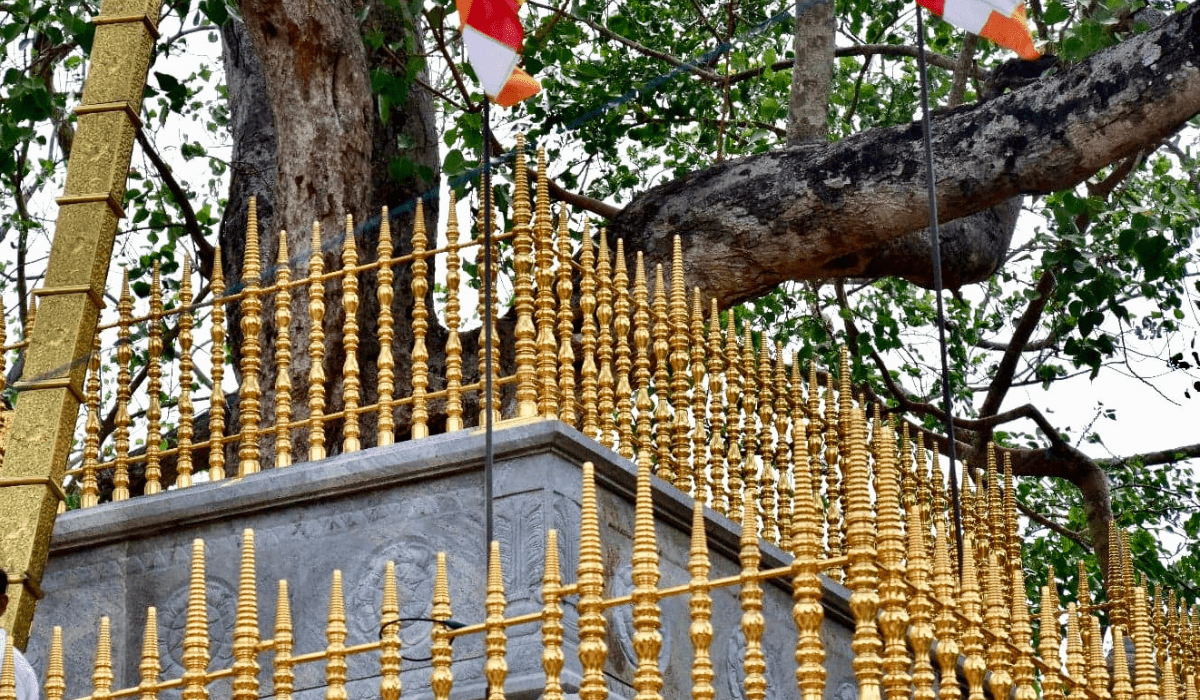
- Sri Maha Bodhi: Planted in 288 BCE, this sacred fig tree is one of the oldest living trees in the world with a recorded history. It is a focal point of worship and reverence for Buddhists.
- Isurumuniya: A rock temple known for its exquisite carvings, including the famous Isurumuniya Lovers, which depicts a romantic couple believed to represent royal figures.

Festivals and Ceremonies
Anuradhapura hosts several religious festivals and ceremonies throughout the year, attracting both locals and tourists. These events provide a glimpse into the rich cultural traditions of Sri Lanka and offer an opportunity to witness traditional rituals and performances.
- Poson Festival: Celebrated in June, this festival commemorates the arrival of Buddhism in Sri Lanka. Pilgrims flock to Anuradhapura to participate in religious observances, processions, and almsgiving.
- Esala Perahera: Although primarily associated with Kandy, the Esala Perahera is also celebrated in Anuradhapura with grand processions and cultural performances. This festival honors the Sacred Tooth Relic of the Buddha and showcases traditional dance and music.
Anuradhapura as a Center for Buddhism
The Spread of Buddhism
Anuradhapura played a pivotal role in the spread of Buddhism in Sri Lanka and beyond. The city’s monasteries and stupas served as centers of learning and pilgrimage, attracting monks and scholars who contributed to the dissemination of Buddhist teachings.
- Mahavihara: Established by King Devanampiya Tissa, the Mahavihara became the main center of Theravada Buddhism in Sri Lanka. It played a crucial role in the preservation and propagation of the Pali Canon, the scriptures of Theravada Buddhism.
- Abhayagiri Monastery: Founded by King Valagamba, this monastery was a center of Mahayana and Vajrayana Buddhism. It attracted scholars from India and other parts of Asia, making it a hub of Buddhist intellectual exchange.

Buddhist Art and Architecture
Anuradhapura is renowned for its contributions to Buddhist art and architecture. The city’s stupas, sculptures, and paintings reflect the artistic achievements of ancient Sri Lanka and continue to inspire admiration and reverence.
- Samadhi Buddha Statue: This serene statue, depicting the Buddha in a state of deep meditation, is considered one of the finest examples of ancient Sri Lankan sculpture.
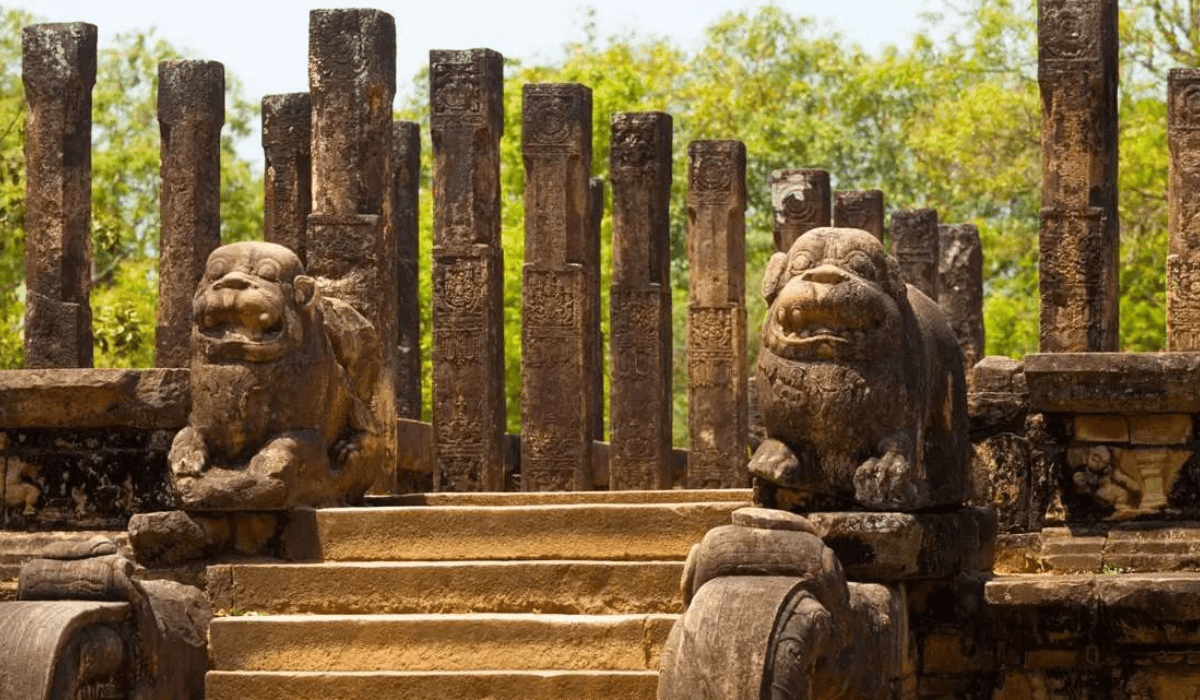
- Moonstones and Guardstones: Unique to Sri Lankan architecture, these intricately carved stones adorn the entrances of temples and monasteries. They depict various religious and mythological motifs, showcasing the craftsmanship of ancient artisans.
Modern-Day Anuradhapura: A Tourist Attraction
Attractions for Tourists
Today, Anuradhapura stands as a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a major tourist attraction in Sri Lanka. The city’s ancient ruins, coupled with its serene ambiance, make it a compelling destination for history enthusiasts, pilgrims, and cultural travelers.
- Exploring the Ruins: Visitors can explore the extensive ruins of Anuradhapura, including its stupas, monasteries, and palaces. Guided tours offer insights into the city’s history and significance.
- Bicycle Tours: One of the best ways to explore Anuradhapura is by bicycle. Numerous rental services are available, allowing tourists to leisurely explore the city’s vast archaeological site.
- Wildlife and Nature: Anuradhapura is surrounded by lush greenery and wildlife. The nearby Wilpattu National Park is a popular destination for wildlife enthusiasts, offering the chance to see elephants, leopards, and a variety of bird species.

Promoting Sustainable Tourism
Efforts are being made to promote sustainable tourism in Anuradhapura, ensuring that the city’s cultural heritage is preserved for future generations. Initiatives include:
- Conservation Projects: Restoration and conservation projects are ongoing to preserve the ancient structures and artifacts of Anuradhapura.
- Eco-Friendly Practices: Promoting eco-friendly practices among tourists, such as minimizing waste and respecting local customs and traditions.
- Community Involvement: Encouraging local community involvement in tourism activities, ensuring that they benefit economically and socially from tourism.
Practical Information for Visitors
Getting to Anuradhapura
Anuradhapura is well-connected by road and rail, making it easily accessible from major cities in Sri Lanka. Regular bus and train services operate between Anuradhapura and Colombo, Kandy, and other key destinations. Private transport options, such as taxis and rental cars, are also available.
Best Time to Visit
The best time to visit Anuradhapura is during the dry season, which runs from May to September. During this period, the weather is generally pleasant, making it ideal for exploring the outdoor ruins and participating in religious activities. However, visitors should be prepared for occasional rainfall and bring appropriate clothing and gear.
Visitor Guidelines
When visiting Anuradhapura, it is important to observe the following guidelines to ensure a respectful and enjoyable experience:
- Dress modestly and cover your shoulders and knees, as a sign of respect for the religious site.
- Remove your shoes and hats before entering sacred areas, such as stupas and temples.
- Refrain from loud conversations and disruptive behavior, to maintain the serene atmosphere of the city.
- Dispose of trash responsibly and avoid littering, to preserve the cleanliness and beauty of the site.



Conclusion
The Kingdom of Anuradhapura is more than just a historical monument; it is a living testament to the enduring legacy of Buddhism in Sri Lanka. With its rich history, cultural significance, and serene surroundings, Anuradhapura offers a unique and enriching experience for visitors seeking spiritual growth and cultural immersion. As a beacon of peace and unity, the city continues to inspire and uplift individuals from all walks of life, making it a must-visit destination for anyone exploring the spiritual and cultural treasures of Sri Lanka.
For those planning a trip to Sri Lanka, a visit to the Kingdom of Anuradhapura promises to be a transformative journey that offers profound insights into the Buddhist way of life and the timeless beauty of this enchanting island nation.




